Manufactured by a series of compression under an extremely high pressure, steel forgings normally have less surface porosity, finer grain structure, higher tensile strength, better fatigue life/strength, and greater ductility than any other steel processing.
Understand the meaning of Forged Steel
The forging process began in the ancient times to produce various kinds of end materials with distinctive properties. In the modern times, machines and hydraulic hammers empower the forging techniques to forge steel and other metals.
Turning the pages back to the historic ages, a forge smith was the protagonist in manufacturing early kinds of forged steel. He used water to first wet the metal and then strike it above an anvil using a forging hammer. Persia and China were the first places where the forging process took its foremost steps. Contemporary methods then started shaping up and acting during the 1800s.
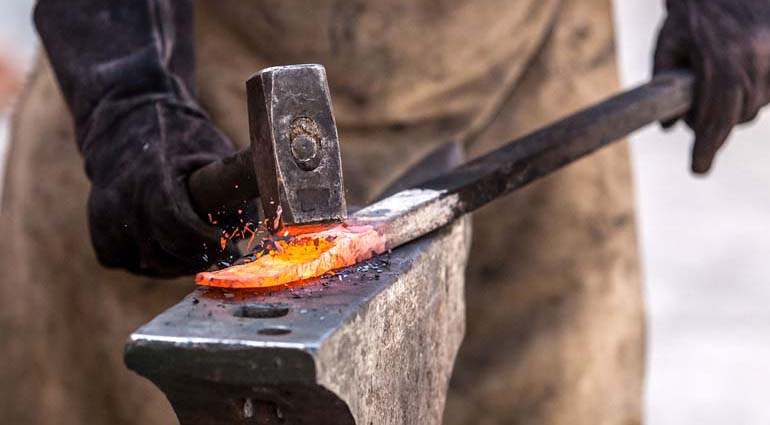

The Process of manufacturing Forged Steel
When steel is heated to forging temperature, it becomes ductile and malleable and be molded to a shape of our choice by applying pressure. With proper processing methods, steel forging allows a billet of steel to be shaped permanently without cracking, due to its plasticity.
Steel forging needs an induction heating system, forge furnace, or forge oven to heat the steel to a sufficient temperature. Metallurgical recrystallization and grain refinement result from the thermal cycle and the deformation process. This strengthens the resulting forged steel product, particularly in terms of impact toughness. It’s weirdly enjoyable to see a giant block of steel get squished and shaped. Interested? Check it out here!
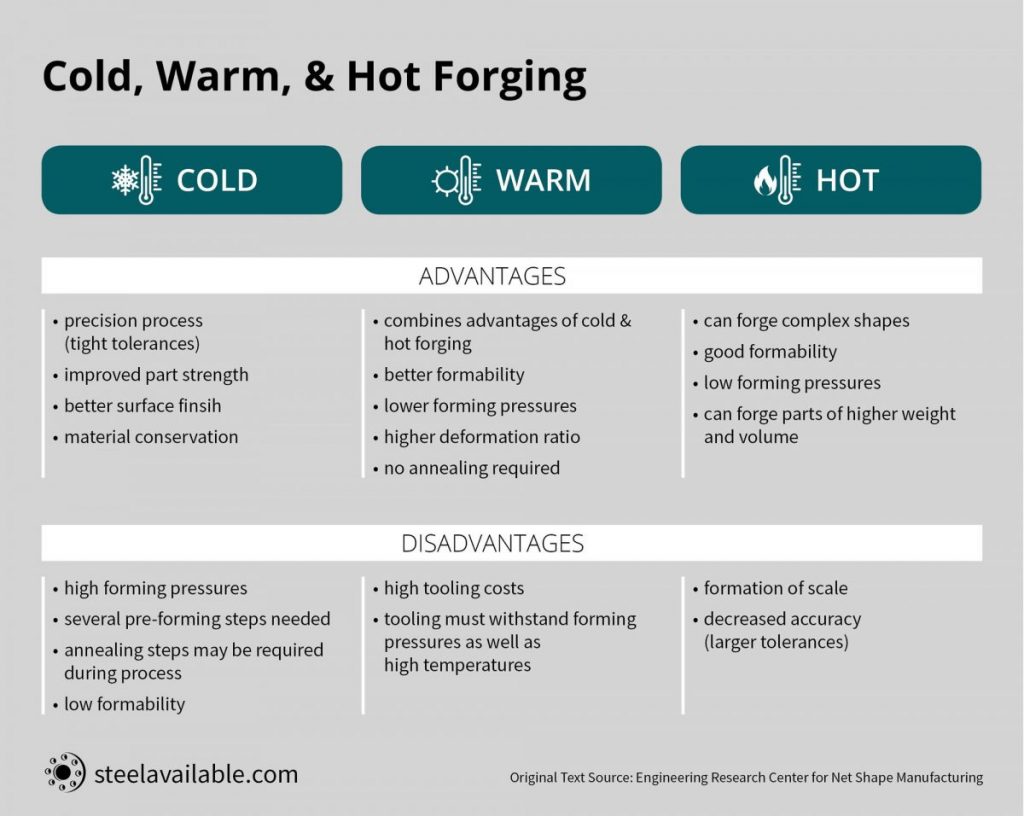
Steel forging can be classified into three categories depending upon the forming temperature:
(1.) Hot forging of steel
The forging temperature is between 950 and 1250 degree Celsius, above the recrystallization temperature. It results in good formability and requires low forming forces.
(2.) Warm forging of steel
The forging temperature is between 750 and 950 degrees Celsius. It leads to limited formability and requires higher forming forces than for hot forging.
(3.) Cold forging of steel
The forging temperature is at room condition, self-heating up to 150 degrees Celsius due to the forming energy. It results in low formability and needs high forming forces.
Interested more in the hot, warm, and cold forging process? Get an insight here!
The Properties of Forged Steel
Forged steel differentiates itself from various other treatments like casting. [2] The properties of forged steel are quite unique when compared to cast steel. Let’s check some of the forged alloy steel properties:
Solidity
Steel forgings constitute to amazing strength, greater toughness, and top-notch durability. On contact with other substances, the steel is less likely to shatter.
Persona
Steel forgings are anisotropic in nature. The strength is not consistent throughout the steel forging. Instead, the strength is the most in the direction of the resulting grain flow when the fabrication process takes place.
Uniformity
One can maintain the same consistency in all the steel forgings manufactured as the forging process is quite meticulous and measured.
Range
There is a limit on the size and the thickness of the steel that can be forged as shaping the metal is quite a tedious job.
The Categories of Forged Steel
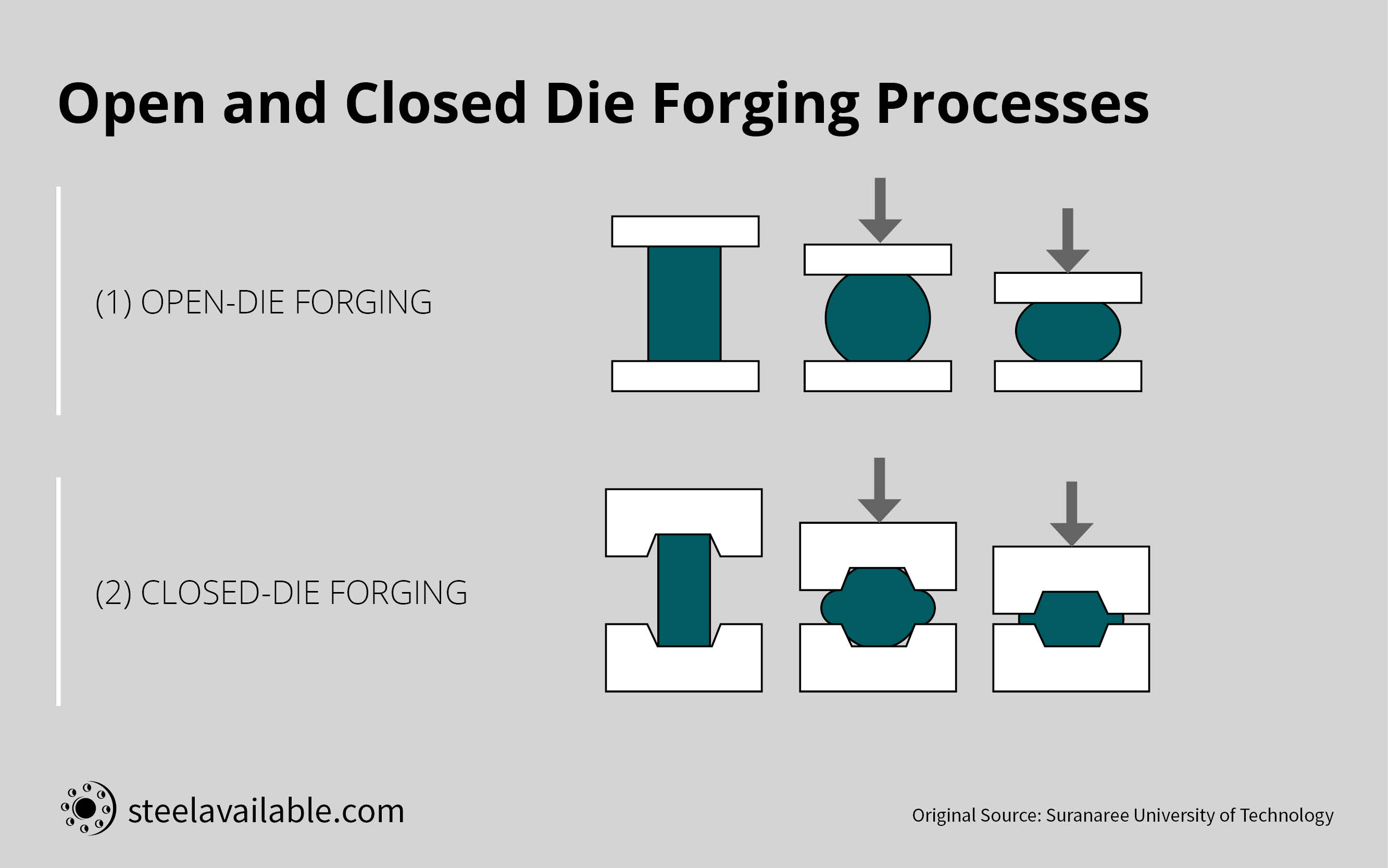
Going deep into the science, steel forging can be classified into two basic types:
(1.) Open Die Forging
In open die forging, the metal piece goes through a deformation between multiple dies that do not enclose the material entirely. The dies constantly hammer the metal to achieve the desired shape.
(2.) Closed Die Forging
In the closed die technique, the metal is pressed between two dies that comprises of the precut profile of the desired shape.
Get more details about the process differences in our article Open Die Forging & Closed Die Forging – What’s the difference?
The Significance of Forged Steel
The bonus of forged steel is that the metal becomes stronger than equivalent types that are cast or machined. Steel forging is commonly used in mechanical and industrial applications due to its strength, availability, and specialized alloy types like stainless steel and carbon steel. Forging in steel offers unsurpassed resilience for manufacturing parts that simply do not fail. The various benefits of forging are:
✔️ Steel forge parts offer a higher degree of reliability and tolerance capabilities
✔️ Steel forgings offer uniformity of composition and structure. They have minimum variation in machinability and mechanical properties
✔️ Forged steel parts are stronger and more reliable than machined or cast parts
✔️ Steel forgings make possible designs that accommodate high loads and stresses
✔️ Steel forgings are used when quality cannot be questioned
✔️ Steel forge parts are free from gas voids, pockets, or cooling defects which can lead to load failure
Want a deep overview on the forged steel advantages?
The Applications of Forged Steel
The characteristics of forged steel such as strength and resistance benefit every industry from automotive to agricultural machinery and manufacturing. Steel forgings serve as pipe fittings in the oil and gas industry whereas as pulleys and gear wheels in the automotive industry. The aircraft industry benefits from the strength of forged steel in their fasteners and airframe members.